Groundwater Geophysics in Hard Rock: Unlocking the Hidden

Groundwater plays a vital role in sustaining life on Earth, providing potable water, supporting ecosystems, and driving economic development. However, in hard rock terrains, accessing and managing groundwater can be a significant challenge due to the complexities of these geological formations.
4.7 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 88540 KB |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 384 pages |
To overcome these obstacles, groundwater geophysics has emerged as an indispensable tool for exploring and characterizing groundwater resources in hard rock environments. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the latest geophysical techniques used in groundwater exploration, highlighting their strengths and applications in hard rock environments.
Geophysical Techniques for Groundwater Exploration
A wide range of geophysical techniques can be employed to study groundwater in hard rock. Each technique offers unique insights based on different physical properties of the subsurface.
Electrical Resistivity Imaging (ERI)
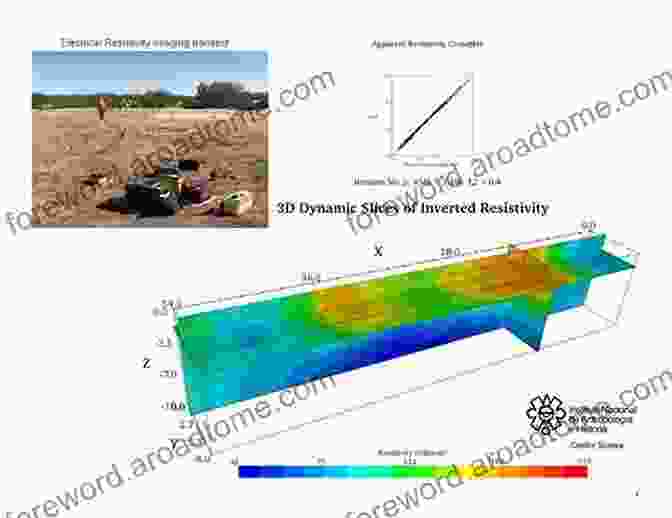
ERI measures the electrical resistivity of the subsurface by injecting electrical currents into the ground and measuring the resulting voltage responses. The resistivity of rocks and fluids varies significantly, allowing ERI to delineate geological structures, identify groundwater-bearing zones, and estimate groundwater quality.
Induced Polarization (IP)
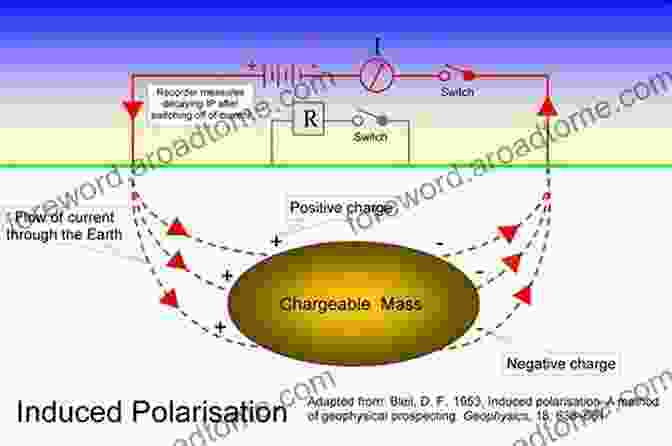
IP is an extension of ERI that measures the electrical response of rocks when a pulsating electrical current is applied. IP is particularly sensitive to the presence of metallic minerals, clay minerals, and groundwater, making it a powerful tool for detecting groundwater-bearing fractures and veins.
Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
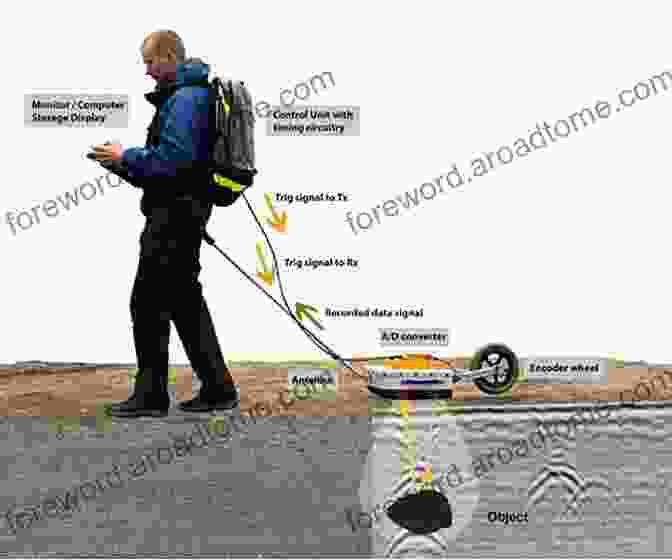
GPR emits high-frequency electromagnetic waves into the ground and records the reflections from subsurface structures. GPR can provide high-resolution images of the subsurface, allowing for the identification of fractures, cavities, and other geological features that may serve as potential groundwater pathways.
Seismic Refraction and Reflection
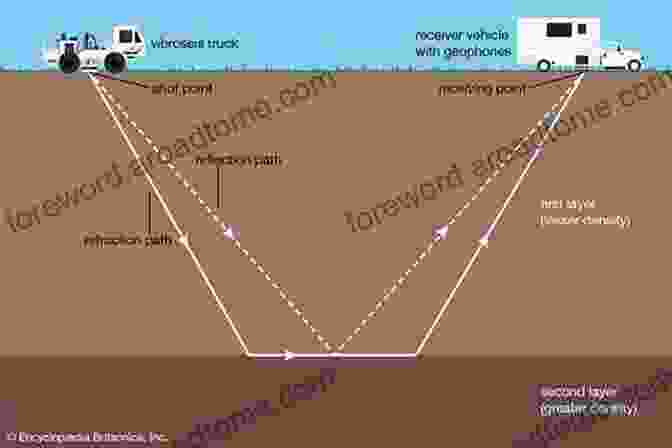
Seismic methods use sound waves to probe the subsurface. Refraction surveys can determine the depth to bedrock and identify subsurface structures, while reflection surveys can provide detailed images of geological layers and structures, including groundwater-bearing aquifers.
Magnetotellurics (MT)
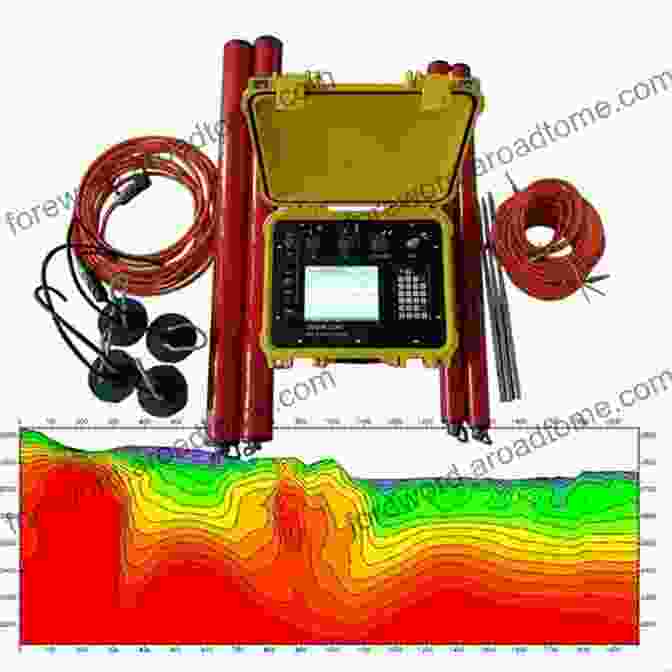

MT measures natural electromagnetic fields in the Earth's crust to study electrical conductivity variations in the subsurface. MT is particularly useful in hard rock environments, where it can provide information on the depth to groundwater, identify geological faults, and characterize groundwater flow paths.
Case Studies in Hard Rock Groundwater Exploration
Groundwater geophysics has been successfully applied in numerous hard rock environments around the world.
- In the Canadian Shield, ERI and IP surveys helped identify groundwater-bearing fractures and veins at a mine site, leading to increased water supply for mining operations.
- In the Arabian Peninsula, GPR and seismic refraction surveys were used to delineate buried wadi channels and identify potential groundwater resources in arid environments.
- In the Western United States, MT surveys were conducted to characterize the electrical conductivity structure of hard rock aquifers, providing insights into groundwater flow patterns and aquifer storage capacity.
Groundwater geophysics has revolutionized groundwater exploration in hard rock terrains, providing valuable data for resource assessment, water management, and environmental protection. By leveraging the latest geophysical techniques, hydrogeologists can gain a deeper understanding of the subsurface and unlock the hidden potential of groundwater resources in challenging environments.
To further delve into the intricacies of groundwater geophysics, our comprehensive book, "Groundwater Geophysics in Hard Rock," offers an in-depth exploration of the subject. This essential guide provides a wealth of knowledge, case studies, and practical applications for groundwater professionals and researchers alike.
With the advancements in geophysical technology and the growing demand for water resources, groundwater geophysics will continue to play a crucial role in ensuring sustainable water management and safeguarding our future water supply in hard rock environments.
4.7 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 88540 KB |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 384 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Edd Morris
Edd Morris Dr Mel Gill
Dr Mel Gill Ed Douglas
Ed Douglas Elena Castrignano
Elena Castrignano Erwin Chemerinsky
Erwin Chemerinsky Melinda R Cordell
Melinda R Cordell Krista A Thompson
Krista A Thompson Dylan Glynn
Dylan Glynn Dr Phillip C Whyte
Dr Phillip C Whyte Terry Donaldson
Terry Donaldson Eleonora Rosati
Eleonora Rosati Meryl Runion
Meryl Runion Elinor Lipman
Elinor Lipman Jason Farley
Jason Farley Maggie Doyne
Maggie Doyne Gillian Straker
Gillian Straker Vicente L Rafael
Vicente L Rafael Efy Enterprises Pvt Ltd
Efy Enterprises Pvt Ltd Jan Chozen Bays
Jan Chozen Bays Fr Mark S Lawlor
Fr Mark S Lawlor
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Connor MitchellUnlock Success with Kiit Thermo 2024 Lecture Notes: A Comprehensive Guide to...
Connor MitchellUnlock Success with Kiit Thermo 2024 Lecture Notes: A Comprehensive Guide to...
 Robert Louis StevensonUnlock the Incredible Mental Benefits of Berries: Science-Based Evidence and...
Robert Louis StevensonUnlock the Incredible Mental Benefits of Berries: Science-Based Evidence and... Isaiah PriceFollow ·4.8k
Isaiah PriceFollow ·4.8k Neil ParkerFollow ·17.4k
Neil ParkerFollow ·17.4k D'Angelo CarterFollow ·18.3k
D'Angelo CarterFollow ·18.3k Junot DíazFollow ·14.4k
Junot DíazFollow ·14.4k Darnell MitchellFollow ·16.9k
Darnell MitchellFollow ·16.9k Jack LondonFollow ·3.8k
Jack LondonFollow ·3.8k Roger TurnerFollow ·17.4k
Roger TurnerFollow ·17.4k Carl WalkerFollow ·5.9k
Carl WalkerFollow ·5.9k

 Reginald Cox
Reginald CoxUnveiling the Extraordinary Life of It Israel Birthday...
A Captivating Narrative of...

 Glenn Hayes
Glenn HayesUnveiling the Enchanting Tapestry of "Tales From The...
Are you ready to step...

 Robert Louis Stevenson
Robert Louis StevensonUnlock the Incredible Mental Benefits of Berries:...
As the sun...

 Edwin Cox
Edwin CoxUnlock the Secrets of Terrain with the Army Map Reading...
Embark on an adventure into the untamed...
4.7 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 88540 KB |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 384 pages |